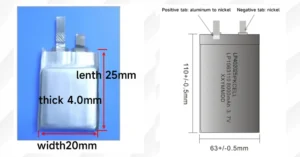
As the demand for portable, high-performance electronics continues to surge, selecting the right energy source has become a critical decision for manufacturers and hobbyists alike. Among the various lithium-based technologies, the Li-Polymer Battery (LP) stands out as a versatile and efficient solution. But what makes it so special, and how do you navigate its technical nuances? Let’s explore why this technology is often the top choice for modern applications.
Table des matières
- How Did Lithium Battery Protection Boards Originate?
- What Is the Basic Structure of a Lithium Protection Board?
- Why Is the IC Considered the “Brain” of the Protection Board?
- How Do MOSFETs Control Charging and Discharging?
- What Role Does PTC Play in Over-Current Protection?
- Why Is Temperature Monitoring with NTC Important?
- Why Are There So Many Types of Protection Boards Today?
- What Does Software-Based Protection Indicate About Industry Trends?
- Where Is Lithium Battery Protection Technology Heading?
How Did Lithium Battery Protection Boards Originate?
How did protection boards become an essential component of lithium battery systems? As lithium batteries began to be widely used in consumer electronics, energy storage systems, power tools and electric mobility, safety challenges became increasingly apparent. Manual monitoring and external safeguards were no longer sufficient. Protection boards were therefore developed to provide real-time monitoring and automatic control, allowing batteries to operate safely under varying conditions without human intervention.
What Is the Basic Structure of a Lithium Protection Board?
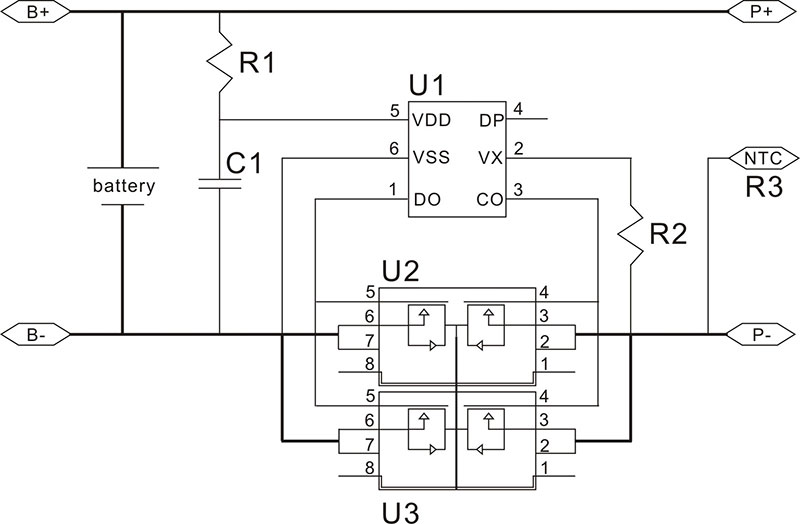
What components make up a typical lithium battery protection board? In a standard lithium battery pack, the system consists of two main parts: the battery cells and the protection board. The protection board itself is composed of multiple electronic components working together, including ICs, MOSFETs, resistors, capacitors, and temperature-sensing elements. Depending on the number of cells connected in series, protection boards can be designed for single-cell or multi-cell configurations, such as three-series battery packs.
Why Is the IC Considered the “Brain” of the Protection Board?
Why is the IC so critical to battery protection? The IC integrates high-precision voltage detection circuits that continuously monitor the battery’s operating status. It determines whether the battery voltage remains within a safe range and initiates protective actions when abnormalities occur.
Over-charge protection is typically triggered when the voltage reaches between 3.9V and 4.4V, while over-discharge protection occurs when the voltage drops to approximately 2.0V–3.0V. Different IC models have different thresholds, making IC selection a key factor in protection board design.
How Do MOSFETs Control Charging and Discharging?
How does the protection board physically control battery current flow? MOSFETs act as electronic switches that regulate charging and discharging paths. They enable or disconnect the battery from the load or charger based on control signals from the IC. In the event of a short circuit or abnormal current, MOSFETs respond rapidly by shutting down the circuit, preventing damage to the battery. Proper selection of MOSFETs requires careful consideration of drain-source voltage (Vds) and maximum current capacity (Id).
What Role Does PTC Play in Over-Current Protection?
Why are PTC components added to some protection boards? PTC devices are made from polymer materials that exhibit self-resetting over-current protection behaviour. Under normal conditions, the PTC remains in a low-resistance state. When excessive current flows through the circuit, heat causes the polymer material to expand, breaking the conductive path and limiting the current. Once the fault condition is removed, the PTC automatically returns to its original state, restoring normal operation.
Why Is Temperature Monitoring with NTC Important?
Why is temperature control just as important as voltage protection? Lithium batteries are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. NTC thermistors are widely used for temperature monitoring because their resistance decreases as temperature rises. By detecting abnormal temperature increases, the protection system can take timely action to prevent overheating. NTC devices are valued for their fast response, high sensitivity and long-term stability in battery applications.
Why Are There So Many Types of Protection Boards Today?
Why has the variety of protection boards expanded so rapidly? As application scenarios become more complex, basic protection functions are no longer sufficient. In addition to standard protection boards, advanced designs now include boards with PTC protection, alloy resistors for temperature control, integrated fuel gauges, and communication interfaces such as RS485, RS232, I²C, and even 4G connectivity. These enhancements enable smarter battery management and improved system reliability.
What Does Software-Based Protection Indicate About Industry Trends?
Why is software-enabled battery protection gaining attention? Software-based protection boards represent the evolution from purely hardware-based safety mechanisms to intelligent battery management systems. By combining hardware sensing with software algorithms, systems can achieve more accurate state-of-charge estimation, fault diagnosis, and data communication, particularly in energy storage and electric vehicle applications.
Where Is Lithium Battery Protection Technology Heading?
Where is the future of lithium battery protection headed? Protection boards are evolving towards higher safety standards, greater integration, and smarter functionality. From basic over-charge and over-discharge protection to fully featured battery management systems (BMS), protection boards are no longer optional components but critical elements that directly influence battery performance, lifespan and market competitiveness.

 Batterie lithium rechargeable par USB
Batterie lithium rechargeable par USB